What Are the Best Techniques for Combining Video with DSLR Cameras?
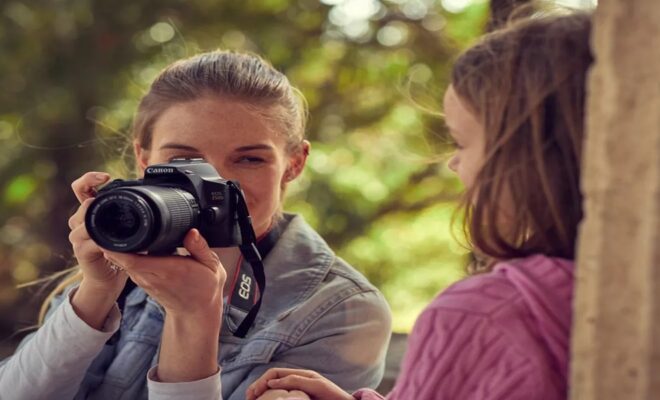

Your video productions will be more versatile and of higher quality if you combine DSLR and video cameras. Using the advantages of both types of cameras can produce better outcomes. To guarantee you get the most out of using a dslr camera and video cameras together, here are some best practices.
Recognising Every Camera’s Advantages
Before delving into optimal methodologies, it is imperative to comprehend the innate advantages of DSLR and video cameras.
DSLR Equip
Image Quality: This is only true if you use pricey dedicated DSLR cameras that pack huge sensors and better-quality lenses.
Depth of Field: They give you more control and this, in turn, allows you to make stunning, dramatic photographs where the background looks very blurry.
Interchangeable Lenses: You may achieve various artistic effects and frame compositions with flexibility when you have the option to swap out lenses.
Video Equipment
Ease of Use: Video cameras include controls and interfaces that are easy to use and optimised for recording videos. They are made for this purpose.
Continuous Recording: Without overheating, they frequently allow longer continuous recording durations.
Audio Capabilities: Professional XLR inputs and other built-in audio features make it simpler to record high-quality audio straight.
Organising Your Shoot
When combining a DSLR and video camera, careful planning is necessary.
Camera Configuration and Setup
When utilising several cameras, proper setup and configuration are essential to getting consistent results.
Congruent Camera Configurations
Resolution and Frame Rate: To preserve visual consistency, ensure both cameras are set to the same resolution and frame rate.
Colour Profiles : To make colour grading in post-production easier, use complementary colour profiles or image styles.
White Balance: To prevent colour differences, manually adjust both cameras’ white balance settings to the same amount.
Timecode Synchronisation
External Timecode Generators: To synchronise the timecode between all cameras, use external timecode generators. As a result, aligning footage during editing is made easier.
Clapboard : To create a visual and aural sync point, use a clapboard or a hand clap at the start of each take.
Methods of Shooting
By using efficient shooting methods, you can be guaranteed to get excellent video from both kinds of cameras.
Multi-Angle Cameras
Primary and Secondary views: To get more artistic photos, use a DSLR for secondary views and a video camera for primary perspectives that allow for continuous filming.
Coverage: To ensure you have enough coverage, record the same scene from several perspectives. It gives you additional editing possibilities.
Motion and Balance
Tripods and Stabilisers: For dynamic pictures, use gimbals or stabilisers; for static shots, use tripods. To prevent shaky footage, make sure both cameras have the proper stabilisation.
Ambience and Audio
Good video production requires both sound and lighting to be done well.
Lighting Methodologies
Equal illumination: Make sure that every camera has the same illumination. To produce equal illumination, use lighting techniques and equipment from a professional source.
Creative Lighting: Make creative use of the DSLR’s versatility in handling various lighting conditions, including low-light and shallow depth-of-field images.
Audio Capturing
External sounds Recorders: To record sounds in high definition, use external audio recorders. Using the visual and audio sync points, synchronise the audio during post-production.
Microphones: Fit the video camera with excellent microphones, and if required, use a different microphone for the DSLR.
Workflow After Production
Optimal post-production procedures guarantee the smooth incorporation of video from both cameras.
Syncing and Editing Video
Multi-Camera Editing: To quickly flip between views and sync footage, take advantage of your editing software’s multi-camera editing tools.
Colour Grading: To create a cohesive appearance, apply uniform colour grading to material shot by both cameras.
Syncing Audio
Automatic Syncing: To match external audio with the video, use the editing software’s automatic syncing tools.
Manual Adjustment: If required, manually adjust the audio sync to guarantee precise synchronisation.
Conclusion:
The combination of DSLR and video cameras can greatly improve your ability to produce videos. You can accomplish professional and cohesive results by knowing the advantages and disadvantages of each camera, carefully organising your shoot, arranging and configuring your equipment, using efficient shooting techniques, ensuring that the lighting and sound are of the highest calibre, and optimising your post-production workflow. By using these best practices, you can make the most of the special benefits offered by DSLR and video cameras to produce visually attractive and engaging content.